-
Die Universität
- Herzlich willkommen
- Das sind wir
- Medien & PR
-
Studium
- Allgemein
- Studienangebot
- Campusleben
-
Forschung
- Profil
- Infrastruktur
- Kooperationen
- Services
-
Karriere
- Arbeitgeberin Med Uni Graz
- Potenziale
- Arbeitsumfeld
- Offene Stellen
-
Diagnostik
- Patient*innen
- Zuweiser*innen
-
Gesundheitsthemen
- Gesundheitsinfrastruktur
Aaroh Anand Joshi
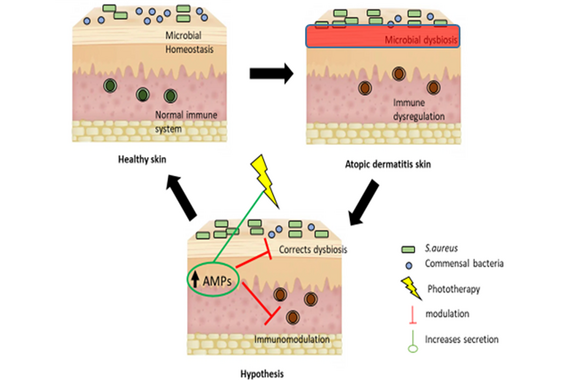
Therapeutic potential of antimicrobial peptides in atopic dermatitis
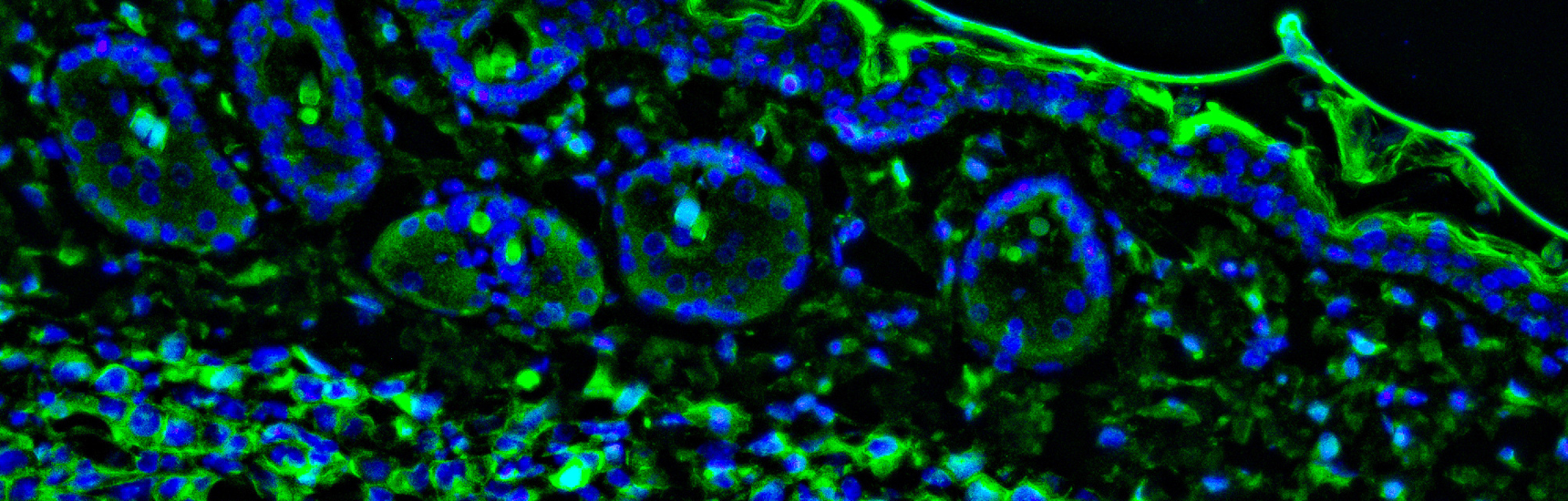
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common, chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by skin barrier dysfunction, immune dysregulation, and microbial dysbiosis which is driven partly by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) colonization. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) (omnipresent small peptides with potent antimicrobial and immunomodulatory function) expression in the skin is further related to microbial dysbiosis observed in AD. Phototherapy (using different wavebands of UV radiation) is a widely used treatment option for AD. We hypothesize that phototherapy in AD patients reinduces AMP expressionwhich normalizes the dysbiotic S. aureus colonization, and the administration of certain AMPs or interference with them may be a therapeutic option to improve AD symptoms.

Autobiography
I graduated from Poona College of Pharmacy, Pune, India in the summer of 2017 with a B.Pharm degree and received a license to practice Pharmacy in India. I further obtained an M.Sc. degree in Pharmaceutical research from Freie Universität Berlin, Germany. My diploma thesis was supervised by Prof. Dr. Sarah Hedtrich. Thereafter I worked in a Skin and Hair research startup in Münster, Germany before joining MedUni Graz as a doctoral candidate. My hobbies include teaching, Cricket, and Yoga.